ORIGINAL STUDIES
BACKGROUND: Osteoporosis is metabolic skeletal disease characterized with low bone mass, bone microarchitecture disturbance that together lead to high prevalence of fragility fractures. Postmenopausal osteoporosis accounts for about 80% of the osteoporosis structure in women over 50 years. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an independent risk factor for low-traumatic fractures. The incidence of both type 2 DM and osteoporosis increases during menopause. Therefore, the study of bone metabolism in experimental diabetes and surgical menopause seems important.
THE AIM of the study was to investigate bone metabolism parameters during menopause and experimental type 2 DM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The half of female Wistar rats had been subjected to bilateral ovariectomy at the beginning of the experiment. Diabetes mellitus (DM) was modelled using a high-fat diet and streptozotocin+nicotinamide. Four weeks after the following groups were formed: «Сontrol» (females without any interventions receiving standard chew, n=5) «OE» (females after ovariectomy n=5), «DM» (females with DM, n=4), «OE+DM» (females after ovariectomy with DM, n=4). The observation period lasted 8 weeks. Bone turnover and calcium-phosphorus metabolism markers (osteocalcin, osteoprotegerin (OPG), nuclear factor-kappa-beta receptor activator ligand (RANKL), sclerostin, fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23), calcium, phosphorus) were measured in the end of experiment. Bone histomorphometry was performed after euthanasia.
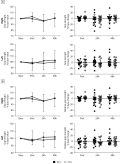
RESULTS: Phosphorus level was significantly lower both in the «OE» group (1.63 [1.58; 1.65] mmol/L) and in the «DM» group (2.81 [2.57; 2.83] mmol /l) compared to the «Control» group (3.12 [2.55; 3.24] mmol/l) (p<0.001). This marker was significantly higher in the «OE+DM» group (2.79 [2.46; 2.81] mmol/l) in comparison to the «OE» group (2.79 [2.46; 2.81] mmol /l), p=0.025. Osteocalcin level was significantly lower in the «DM» group (8.1 [7.8; 9.2] ng/ml) compared to the «Control» group (16.97 [14.07; 17.07] ng/ml ), p=0.005. A weak negative correlation (r= -0.5, p<0,05) was found between glucose and osteocalcin levels (p=0.03). RANKL level was significantly lower in the «OE+DM» group (278,1 [273.1; 289.7] pg/mL) compared to the «OE» group (400.6 [394.5; 415.1] pg/mL), besides the OPG/RANKL ratio was higher in this group (0.03 [0.02; 0.035] and 0.01 [0.004; 0.014], respectively), p=0.05. In the «OE» group lower OPG level (5.1 [1.5; 5.6] pmol/L) and OPG/RANKL ratio (0.01 [0.003; 0.014]) were obtained in comparison to the «Control» group (12.3 [8.8; 14.2] pmol/l and (0.34[0.33; 0.4], p=0.025 and p=0.07, respectively. The area of bone trabeculae in the epiphyseal zone was the largest in the «Control» group (42 [39; 45]) %; the difference was significant compared to the «OE» group (29 [25; 33] %, p=0.011) and the «OE+DM» group (30 [23; 25] %, p=0.016). The area of bone trabeculae in the metaepiphyseal zone was also the largest in the «Control» group (49 [46; 52] %) compared to the «OE» (35 [25; 39] %), «DM» (31 [26; 34] %), «OE+DM» (35 [33; 38] %), p<0.001. There was no difference in the thickness of the bone trabeculae among the groups.
CONCLUSION: DM induction can significantly inhibit bone remodeling in animals without menopause, which is reflected in a lower osteocalcin level. Bone turnover during DM and surgical menopause is characterized by lower RANKL levels and higher OPG/RANKL ratio. The effect of ovariectomy on bone metabolism was manifested in more extensive decrease in bone trabeculae area than in DM.
BACKGROUND: Heart rate autonomic regulation can go out of balance which is normally assessed by the heart rate variability (HRV) indices. Similarly, it is relevant to research if and how HRV fluctuations can be influenced by varying signs of insulin resistance since they are quite common in Northern men. At present, there is no evidence of this influence in the North residents of older ages.
AIM: This study aimed to comparatively assess heart rate variability in mature men who do or do not feature metabolic signs of insulin resistance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seventy-three mature aged male residents of Magadan Region, Caucasian by origin, were examined. All the subjects were divided into two groups: Group without insulin resistance signs (HOMA-IR index < 2.5 units) and Group with insulin resistance signs (HOMA-IR index > 2.5 units). We used immunochemiluminescent and enzymatic methods, and heart rate variability was assessed using the Varikard (Russia).
RESULTS: Our research showed that 48% of all the examinees exhibited signs of insulin resistance along with an increase in the sympathetic activity in heart rate regulation. We also identified the heart rate indicators that had proved to undergo the most significant changes depending on the HOMA-IR index and the presence or absence of signs of insulin resistance: MxDMn, pNN50, SDNN, AMo50, SI, TP, HF, LF, and Body Mass.
CONCLUSION: In general, the results obtained allow for ascertaining the high proportion of male Northerners of mature age with signs of insulin resistance. We also claim that those examinees demonstrate an autonomic imbalance and a moderate dominance of the sympathetic activity with a simultaneous decrease in activation of the parasympathetic link of autonomic nervous system and high body mass variables. At the same time, the correlations and causal associations among signs of insulin resistance, activation of the sympathetic link of autonomic nervous system, and overweight remain unclear. Apparently, all the analyzed features are likely to complement each other rather than completely exclude each other. The triad of obesity, signs of insulin resistance, and activation of the sympathetic link of autonomic nervous system is a driving factor for significant health risks. This study is expected to spread the use of the method of assessing heart rate variability based on insulin resistance signs as well as in reliance on metabolic disorders in general in a sample of mature men.
BACKGROUND: Obesity, expressed as a high body mass index (BMI), is associated with a risk of decrease in functional capacity and muscle strength, in particular in weight-bearing joints, but so far, no study has been able to show a sufficiently strong relationship between these factors. two options in conclusion.
AIM: This study was conducted to quantify the effect of intense exercise on the functional capacity and muscle power of obese individuals and the risk of knee osteoarthritis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The present research project is characterized as a clinical trial, cross-sectional, and uncontrolled research. All participants had a body mass index from 30.6 kg/m² to 34.9 kg/m² and reported not working out in the last 3 months prior to this experiment. Before their involvement, all participants were informed during an initial interview about the experimental procedure, the nature of the research, and the test protocols. They gave their written and signed informed consent to voluntarily participate in this research and completed two questionnaires. Participants in our study were recruited from sports centers, social clubs, and word of mouth. A total of 78 participants responded to the call articipated in our training protocol which was composed of two main parts. The first one is the «Anthropometric measurements tests» and the second one is the «Functional capacity tests» that were done in a gym. The participants were divided randomly into two experimental. After the end of every phase of the experiment, some members of each group were moved randomly to the other group.
RESULTS: The final results of the intra-class correlation coefficient measurements for a set of tests showed strong reliability among members of each examined group. For the handgrip strength tests of the right and left hands, the results were 0.850 and 0.892, respectively. For the squat jump and countermovement jump tests, the results were 0.966 and 0.932, respectively. The results were 0.896 and 0.945 for walking 6 meters with or without double tasks. Finally, for the TUG and TUP-DT tests, the results were 0.520 and 0.663, respectively. After analyzing and interpreting the data for the functional capacity tests, the following results were obtained: For the 5 sit-stand test, the result was (F (3.87)=4.22; p=0.008, ηp2=0.127). For the Time up and go test, the result was (F (3.87)=4.56; p=0.019, ηp2=0.136), and for the 6 m walk, the result was (F (3.87)=3.81; p=0.013, ηp2=0.116). Finally, the 5X sit-to-stand test at 48 hours was lower than the base value (p=0.024), while the TUG immediately after the post was lower than the base value.
CONCLUSION: In conclusion, the results of this study demonstrate the positive impact of intense exercise on muscle power and functional capacity in obese individuals. These findings suggest that high-intensity physical activity may be an effective means of improving the health and quality of life of obese individuals. Therefore, it is recommended that obese individuals include high-intensity exercise in their regular exercise program to reap these health benefits. However, it is important to emphasize the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before starting a high-intensity exercise program to avoid the risk of injury or health complications.
BACKGROUND: In men, obesity is accompanied by a complex of metabolic and hormonal disorders, which leads to androgen deficiency and impaired spermatogenesis. Antidiabetic drugs, including metformin (MF), and luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) agonists, which activate testicular steroidogenesis, can be used to correct reproductive dysfunctions. However, in diet-induced obesity (DIO), their effectiveness and mechanisms of action are poorly understood.
AIM: In men, obesity is accompanied by a complex of metabolic and hormonal disorders, which leads to androgen deficiency and impaired spermatogenesis. Antidiabetic drugs, including metformin (MF), and luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) agonists, which activate testicular steroidogenesis, can be used to correct reproductive dysfunctions. However, in dietinduced obesity (DIO), their effectiveness and mechanisms of action are poorly understood.
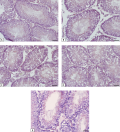
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Obesity in male Wistar rats was induced by a 23-week diet enriched with saturated fats. MF treatment was carried out for 5 weeks at a dose of 120 mg/kg/day (orally), and the treatment with hCG and TP03 was carried out for 5 days at daily doses of 20 IU/rat (s.c.) and 15 mg/kg (i.p.), respectively. Using microscopy and histochemical analysis, the number and motility of spermatozoa (SP), the number of their defective forms and the morphology of the seminiferous tubules were assessed, and the levels of testosterone and other hormones in the blood were measured using ELISA.
RESULTS: MF, hCG, and TP03 to varying degrees increased the number of SP and the proportion of their mobile forms, including those with forward movement, which were reduced in DIO rats, and also normalized the thickness of the epithelium of the seminiferous tubules and the number of spermatogonia and pachytene spermatocytes in them, but did not reduced the proportion of defective forms of SP, increased in DIO. In the case of MF, this was associated with the drug-induced normalization of body weight, glucose tolerance, and the insulin and leptin levels in DIO rats. The positive effect of hCG and TP03 on spermatogenesis was due to their stimulating effect on testosterone production.
CONCLUSION: The use of long-term MF therapy and short-term courses of LHR-agonists normalizes impaired spermatogenesis in DIO, which indicates the prospects for their use to improve male fertility in obesity, and in the case of MF therapy, normalization of the metabolic and hormonal status is of great importance, while in the case of LHR-agonists the most important factor is their steroidogenic effect.
BACKGROUND. Among the many causes of obesity, genetic factors occupy a special place. An obvious role among them belongs to the genetic polymorphism of lipid metabolism enzymes, including paraoxonase-1 (PON-1). Until now, the character of the relationship between PON-1 polymorphism and the state of the endocrine function of mesenchymal tissues remains unclear. Its study will clarify the subtle mechanisms of the development of obesity in childhood and adolescence.
AIM. The aim of the study was to investigate the relationship between PON-1 polymorphism (rs662) and changes in the content of adipokines, myokines, and blood lipid metabolism in children and adolescents of different sexes with obesity.
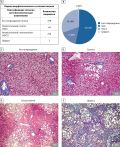
MATERIALS AND METHODS. In 100 healthy children and adolescents of different sexes and 89 of their peers with obesity, a genetic study was conducted to assess the single nucleotide polymorphism of the PAO-1 (rs662) genes. In blood serum, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, triacylglycerols, glucose and aminotransferase activity (alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase) were determined by photometric methods, as well as leptin, adiponectin, resistin, apelin, irisin, adipsin, myostatin, FGF21, osteocrine, oncostatin and insulin — by multiplex ELISA, and asprosin — by ELISA ones.
RESULTS. The patients with the homozygous Arg192/Arg allele, the development of complications of obesity in boys is limited and their occurrence in girls is prevented. In other variants of PON-1 polymorphism (Gln192/Gln and Gln192/Arg genotypes), protective mechanisms are formed in the body of girls aimed at preventing complications in obesity. In boys with the Gln192/Gln genotype, obesity reveals more pronounced shifts in lipid metabolism, manifestations of alteration and an increase in the mass of adipose tissue, and in boys-carriers of the heterozygous Gln192/Arg allele, atherogenesis processes increase.
CONCLUSION. Polymorphism of the paraoxonase-1 gene (rs662) contributes to the appearance of gender differences in changes in the content of adipokines and myokines in the blood during obesity in childhood and adolescence.
REVIEW
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a liver disease with a characteristic accumulation of fatty inclusions in hepatocytes and includes a spectrum of liver lesions from steatosis to cirrhosis. In view of the increasing incidence of obesity and associated NAFLD, a search is underway for optimal treatments. The authors analyzed published clinical studies on the effect of bariatric surgery on morphological changes in the liver. The literature was searched for the keywords «non-alcoholic fatty liver disease», «obesity», «bariatric surgery» in Pubmed databases and еLibrary.ru for the period from 1990 to 2022 . Both the positive effects of surgical treatment of obesity in the form of a decrease in steatosis, steatohepatitis of the liver, and adverse effects in the form of aggravation of cirrhosis in patients after surgery are considered. Despite the obvious effectiveness of bariatric surgery in relation to the components of the metabolic syndrome associated with obesity, there is still no unambiguous opinion about their effectiveness in relation to NAFLD.
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem are adult stem cells endowed with multipotent abilities and immunomodulatory properties, like mesenchymal stem cells of other origins. Numerous studies show that adipose tissue stem cells are involved in the pathological process and can exhibit pro-inflammatory properties and attract inflammatory immune cells in the neighborhood. Subsequently, inflammation creates a microenvironment leading to adipose tissue dysfunction. Examples of such a process are obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, in which adipogenesis is disrupted and insulin resistance is initiated. The aim of this review is to understand the role of adipose tissue stem cells in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
One of the causes of non-tumor related hyperprolactinemia is taking a medications. Physicians of various specialties, such as cardiologists, gastroenterologists, endocrinologists, and neurologists, encounter hyperprolactinemia as a side effect of drug therapy in their practice, but it is most often observed in the practice of a psychiatrist when treating patients with psychotropic medications. Over the past few years, there has been an increase in the frequency of prescriptions of antidepressants and neuroleptics due to post-COVID-19 syndrome, anxiety and stress caused by the pandemic of a new coronavirus infection. There is also a predisposition to the development of hyperprolactinemia on the background of taking neuroleptics due to genetic features of patients. Currently, there is no established common algorithm for diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced hyperprolactinemia in the world. Based on a review of foreign and domestic literature, the article discusses in detail the mechanisms of development and various approaches to the correction of iatrogenic (drug-induced) hyperprolactinemia, assesses the prolactogenic activity of neuroleptics, and proposes algorithms for prolactin monitoring and correction of hyperprolactinemia using dopamine agonists. Often the tactics of management of such patients need to be discussed by a team of specialized physicians.
Iron affects the pathogenesis and clinical course of several chronic metabolic diseases such as obesity, atherosclerosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. High pro-oxidant iron activity is physiologically controlled by mechanisms regulating entry, recycling, and loss of body iron. These mechanisms include the interplay of iron with ferritin, transferrin, hepcidin, insulin, as well as with adipokines and proinflammatory molecules. An imbalance of these regulatory mechanisms results in both systemic and parenchymal siderosis. Iron overload has a toxic effect on the major tissues involved in lipid and glucose metabolism — pancreatic β cells, liver, muscle, and adipose tissue — as well as the organs affected by chronic hyperglycemia — brain, retina and kidneys. Hyperferremia leads to a decrease in insulin secretion, the formation of insulin resistance and increased liver gluconeogenesis. Molecular mechanisms for these effects are diverse. Elucidating them will implicate both for carbohydrate metabolism disorders prevention and for the pathogenesis of other diseases that are, like diabetes mellitus type 2, associated with nutrition, aging and iron. The literature review presents data from world studies on the mutual influence of glucose metabolism and iron overload, and discusses the differences between hereditary and acquired disorders of iron metabolism from the standpoint of their influence on carbohydrate metabolism.
CASE REPORT
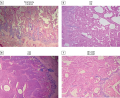
This article presents a non-standard clinical case of non-obvious causes of secondary osteoporosis in the routine practice of an outpatient and inpatient endocrinologist. This work demonstrates a rather rare situation, including the identification of atypical clinical manifestations of osteoporosis in a patient, namely the presence of a young man with complaints of general weakness, severe pain in the spine, forcing daily use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, decreased motor activity, and laboratory indicators such as hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria against the background of reference values of parathyroid hormone, hyperproteinemia and increased ESR. Taking into account the clinical picture described above, an integral part of a further correct diagnostic search is the exclusion of endocrine diseases that cause a decrease in bone mineral density. In parallel, the initiated prescription of pathogenetically based treatment of secondary osteoporosis is an important component of this disease. The use of such a multidisciplinary approach led to timely verification of the underlying oncohematological disease and routing the patient to a specialized hospital and made it possible to prevent irreversible changes associated with a critical decrease in bone mineral density and improve the patient’s quality of life.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2306-5524 (Online)